The States of Matter in our surroundings are generally of 3 types that are Solid, Liquid, and Gas. Each states of matter have its own properties and characteristics. Before understanding the states of matter we should first understand the meaning of matter.
Matter and its Physical Nature
In a simple explanation, we can say that matter is anything that occupies space and has a mass that our body can sense are called matter. In our daily life, everything we are surrounded with are matter for example Desk, Table, Water, Air etc.
In modern science, matter is basically divided into its Chemical Properties and its Physical Properties. So, the reactivity, rust, combustion, etc are its chemical properties, and the colour, hardness, boiling point, melting point, density, etc are its physical properties.
In the Physical Nature of matter, we have found that all the matter around us is made of different particles having their certain shape, size, and properties. And the size of the particles is very small beyond our imaginations.
Characteristics of Particle of Matter
There are mainly four Characteristics of Particles of Matter.
- There is the space between all the particles in the matter.
- All the particles in the matter possess some energy due to which they are in constant motion such type of energy is called Kinetic Energy. With the increase in temperature, the Kinetic energy of the particle increases.
- Every particle in the matter have the tendency to intermix of its own between the spaces. When the particles of two different matter intermix with each other on their own such a process is called diffusion.
- There is a force of attraction between the particles of the matter such attraction is called intermolecular force of attraction. These forces of attraction vary on different matters.
Read More: Change of State of Matter Detailed Explanations.
States of Matter
All the matters we see in our daily life generally exist in the Three States that are Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous. The existence of different states of matter is based on the properties and characteristics of particles.
Solid State
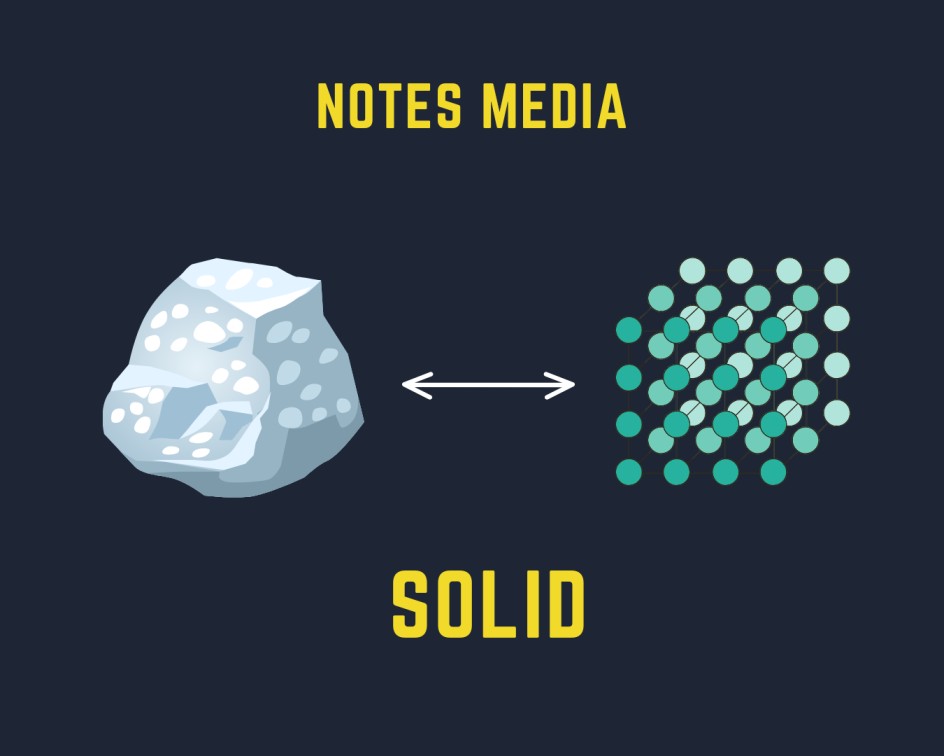
Solid is defined as the state of matter having a definite shape and volume and possessing rigidity and compressibility.
Properties of Solid State
- The process of diffusion in a solid is a negligible and very slow process.
- Solids have definite shapes, volumes, and boundaries.
- Solid have the property to maintain their shape when an external force is applied to it. For Example, When we pull the rubber bands they lose their shape until the force is applied but when the force is removed they regain their shape again.
- There is a strong intermolecular force between the particles so it is difficult for the solid to break under the force.
- The solid has higher density in comparison to other states that are liquid and gaseous.
Note: The tendency to flow by any form of matter comes in fluid. For Example Liquids and Gases.
Liquid State
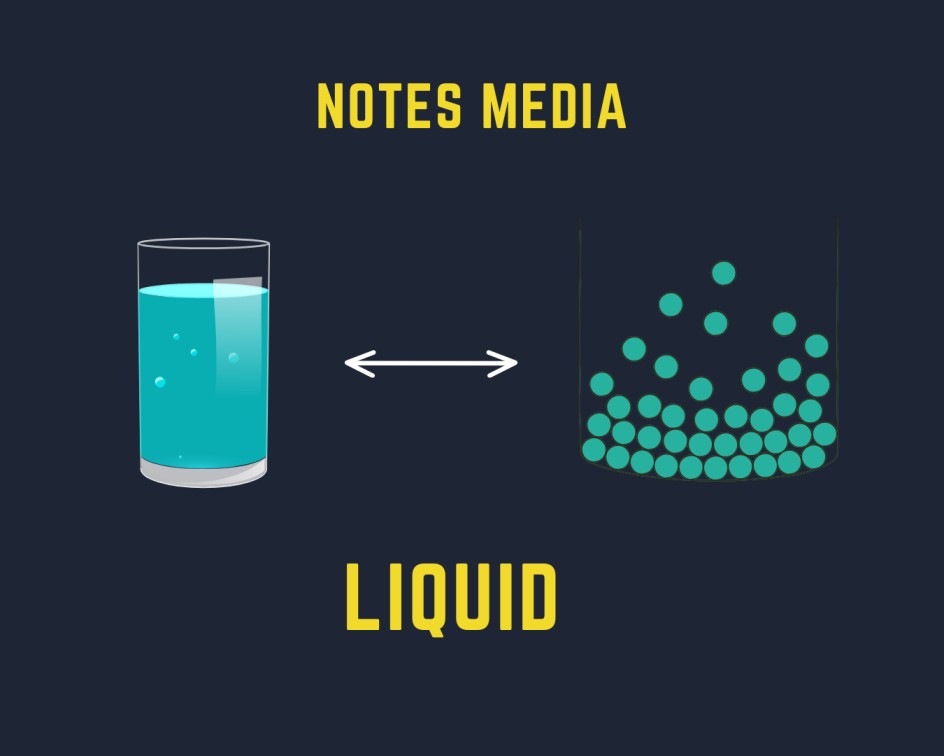
Liquid is defined as the state of matter having a fixed volume but not a fixed shape.
Properties of Liquid State
- In the Liquid state all the Solid, Liquid, and Gas diffuse easily. An example of a Solid diffused in the liquid is the solution of Sugar / Salt in the water. An example of a liquid diffused in the liquid is when the acid in the Liquid form is mixed with water to form a dilute solution. An example of Gas diffused in the liquid is all the water bodies have oxygen already diffused in the water due to which aquatic animals can breathe easily.
- Liquids have definite volumes but they do not have definite shapes because we can make any shape by putting it in different shape containers or vessels.
- Liquids are not rigid in nature due to which they can flow and change shape so we can also be called fluid.
- Liquids are almost incompressible in nature.
- The intermolecular force of attraction between particles in a liquid is higher than that of gas and lower than that of a solid.
- The rate of diffusion of liquid is higher than the solid and lesser than the gas because of the greater space between them in the particle.
- The density of the liquid is less in comparison to solid but some of the cases are exceptional for example ice.
Gaseous State

Gaseous is defined as the state of matter having no fixed shape and no fixed volume.
Properties of Gaseous State
- Gaseous show the highest property of diffusion in comparison to solid and liquid because of the large free space between particles. For example, we can easily smell the hot cooked food prepared in other rooms, the Fragrance of the incense stick, etc.
- Gaseous does not have a definite shape and volume because of weak intermolecular force between the particles.
- Gaseous are highly compressible in nature due to which we can store the large volume of gas in the container. For Example, LPG (Liquified Petroleum Gas) is used in every house compressed petroleum gas in large quantities in the cylinder. Same as with CNG (Compressed Natural Gas).
- The movement of the particle is higher in the gaseous state because of which gas exerts higher pressure on the wall of containers.
- Gaseous shows the tendency of flow due to which it also comes under fluid.
Social Link of our Page
- Instagram: Click Here
- Whatsapp Community: Click Here
- Youtube: Click Here







1 thought on “States of Matter: Solid, Liquid, and Gas Definition and Properties”